Top 5 Foods Highest in Vitamin E
Since vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin, it’s logical to find it in foods rich in fats and certain oils. Here are five foods or groups of foods where you can find vitamin E.
Vegetable oils

Vegetable oils contain essential fatty acids: omega-3 and omega-6, which are good for brain function. They have high levels of vitamin E:
- Sunflower oil: 75 mg/100 g
- Canola oil: 42 mg/100 g
- Olive oil: 25 mg/100 g
- Hazelnut oil: 49 mg/100 g
Ideal for making dressings, vegetable oils should preferably be consumed cold. They can also be used for pan frying. Measure with a tablespoon (one to two tablespoons are enough) to avoid excess.
Nutty dried fruits

Almonds, hazelnuts, Brazil nuts are rich in vitamin E. Almonds provide approximately 15 mg/100g, while hazelnuts and nuts account for 3.5 to 8 mg/100 g. Not negligible!
Dried fruits are suitable for snacks, as they are convenient and tasty. However, consume them in moderation as their calorie content can be significant.
Nutritionists recommend eating a handful of dried fruits at snack time. They can also be crushed to sprinkle over composed salads. It’s delicious!
Fatty fish

Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are healthy foods. They contain omega-3 and other essential nutrients for maintaining the body’s function, including vitamin E (content: 0.3 to 2 mg/100 g).
Fatty fish can be served grilled, baked in parchment, or roasted. These cooking methods are fat-free. Although they are healthy, it’s preferable to consume fatty fish only once to three times per week.
They are easily paired with grilled vegetables and a portion of starch: potatoes, rice, whole grain pasta, for a balanced and healthy meal.
Dried apricots and prunes
Dried fruits like apricots and prunes are tasty. They contain 2 to 4 mg of vitamin E, for every 100 g of food.
Like nutty dried fruits, they can be reserved for a small snack. To limit sugar additions, one can opt for homemade preparations as industrial dried fruits contain added sugars. This also helps to limit calorie intake. Dried fruits are delicious served with a portion of yogurt.
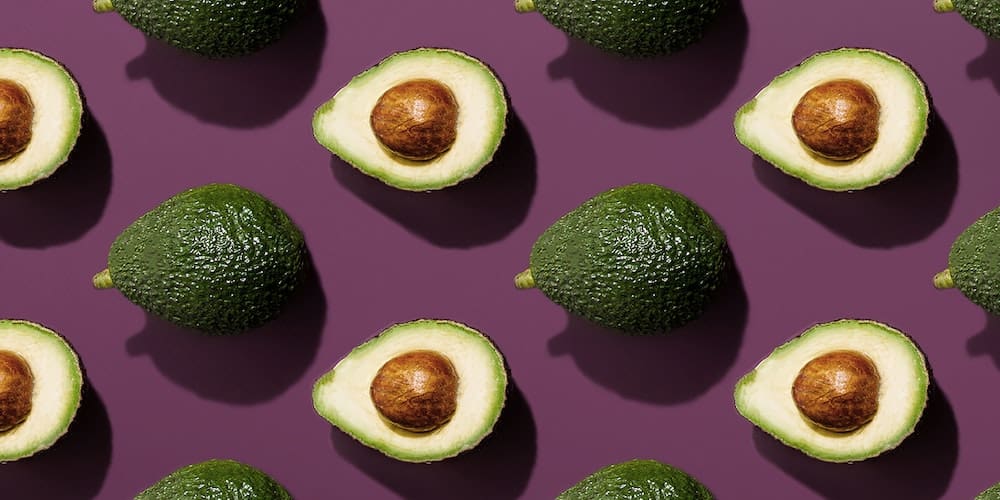
Avocado

Avocado sometimes has a bad reputation and not for good reasons! Considered too fatty, too rich, it actually contains good fats and can be consumed regularly without ‘causing weight gain’. It represents a natural source of vitamin E.
Avocado is mainly consumed as an appetizer, in salads mixed with other foods (tomatoes, eggs, corn…). Or simply spread on bread!
It can be served with a citrus sauce or a sauce based on vegetable oil (canola, hazelnut, olive, or sunflower oil) to multiply the nutritional benefits. Remember, tocopherol being fat-soluble, is better absorbed during a meal containing fats.
Storage: Vitamin E is sensitive to light. It degrades during prolonged exposure. Therefore, foods containing it should be kept away from light to preserve their nutritional qualities.
Description and Role of Vitamin E
Vitamin E was discovered in 1922 by embryologist Herbert MacLean Evans and his assistant Katharine Scott Bishop in California. The two scientists were conducting experiments on the gestation of rats. The compound, eventually named vitamin E, proved to be essential for fetal development.
In 1924, a new study conducted on rats demonstrated that vitamin E was crucial for the fertility of the animals. It was thus also named tocopherol (from the Greek tocos: offspring, pherein: to carry) to emphasize this function.
However, it wasn’t until 1968 that it was recognized as an essential nutrient for human life.
Vitamin E is present in eight natural forms. There are 4 forms of tocopherol and 4 forms of tocotrienol, distinguished by the addition of Greek letters as a prefix: alpha, beta, gamma, delta. The active form of vitamin E is alpha-tocopherol.

This vitamin performs several roles and works in synergy with various elements present in the body. Its functions are as follows:
- Has antioxidant properties. Indeed, it acts against cell and tissue aging by limiting the production of free radicals. It has a complementary action with selenium and beta-carotene.
- Preserves membrane lipids, good cholesterol, and limits the clumping of blood platelets by exerting an anti-inflammatory action and promoting the synthesis of substances that affect vasodilation. This function helps limit atherosclerosis, which results in preventing the onset of cardiovascular diseases.
- Preserves the immune system.
- Has a repairing effect on the skin, thanks to its antioxidant properties. It also helps maintain the elasticity and plasticity of the skin.
- Might have a protective effect on cognitive functions and vision by preventing cataracts and AMD (age-related macular degeneration). Studies are still ongoing to prove these potential functions.
Signs of vitamin E deficiency
It is rare to observe vitamin E deficiencies in adults. Daily requirements are usually met through a good diet. Cases of deficiency are more commonly found in premature babies or young children.
They can be caused by diseases that lead to fat malabsorption or by digestive disorders.
Symptoms of vitamin E deficiency:
- Hemolytic anemia (in babies or young children). This disease is linked to a hemoglobin defect and results in the destruction of red blood cells.
- Nerve damage and muscle weakness
- Coordination or movement disorders
- Decrease in visual acuity
In case of underdosing, the doctor prescribes supplementation either orally or intravenously depending on the symptoms observed. In this scenario, self-medication should be avoided as it can be dangerous.
Recommended daily vitamin E needs
As with every nutrient, it is necessary to ensure regular intake of vitamin E. Here is a summary of the recommended daily needs:
- Babies aged 0 to 1 year: 4 to 5 mg/day
- Children aged 1 to 3 years: 6 mg/day
- Children aged 4 to 6 years: 7 to 7.5 mg/day
- Children aged 7 to 9 years: 7.5 to 9 mg/day
- Children aged 10 to 13 years: 11 mg
- Adolescents from 14 years and Men: 15.5 mg/day
- Adolescent girls from 14 years and Women: 10 mg/day
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: 12 mg/day
- Athletes: Up to 24 mg/day
- Men and Women (> 75 years): recommended intake of 20 to 50 mg/day
Hazards, side effects, and overdoses of vitamin E
The body can store vitamin E. It is generally stored in the adipose tissue due to its fat-soluble nature. Thus, vitamin E overdose is possible.
It is considered that the limit dose is reached when adding 50 mg/day to the recommended daily dosage, which is over 60 mg/day for an adult woman, for example.
An intervention study reportedly demonstrated that a high intake of vitamin E might have an impact on the occurrence of strokes (slight increase in strokes among a group of subjects supplemented with 50 mg/day of vitamin E over 5 years). However, further studies are still needed to confirm this hypothesis.
Advice: before any vitamin supplementation using dietary supplements, it is preferable to consult your doctor.
Medical supervision along with associated biological monitoring may be necessary to avoid any complications related to intake.



