BENEFITS OF CAMELINA
✓ Improves skin beauty
✓ Antioxidant
✓ Anti-inflammatory
✓ Reduces cholesterol levels
✓ Improves diabetes
What is camelina?
Native to Northern Europe and Central Asia, camelina (Camelina sativa) is also known as ‘false flax’ or ‘German sesame.’ Like rapeseed, mustard, or watercress, it belongs to the Brassicaceae family. It can reach a height of 80 cm and produces yellow flowers, similar to those of rapeseed.
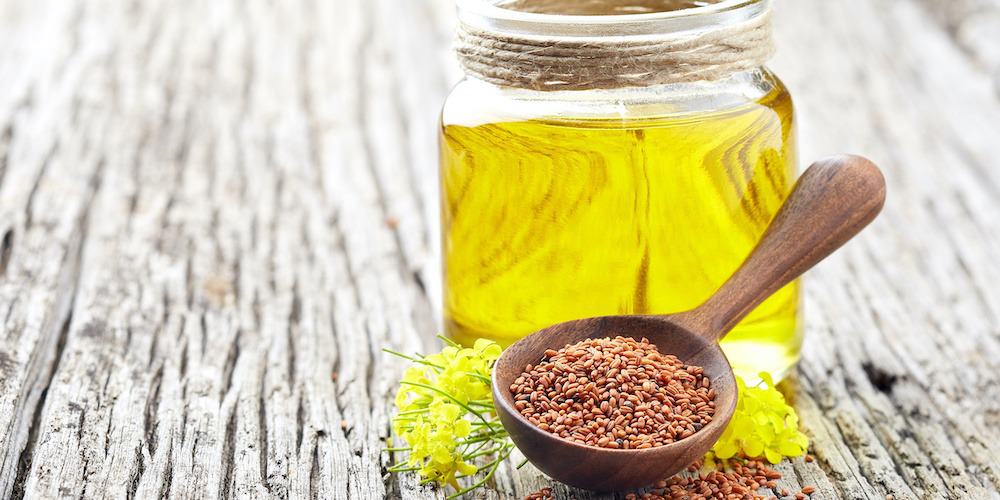
Camelina is an oilseed plant whose seeds are pressed to extract oil. This yields a golden-yellow vegetable oil with a subtle and ‘green’ aroma. It is used both in cooking and cosmetics.
Its seeds are also edible and can be consumed as is. Additionally, it is used to produce a gluten-free flour.
Long forgotten, camelina is making a comeback today, driven by the growing demand for protein crops: faba bean, lupine, sunflower… It stands out for its high content of fatty acids (omega-3-6-9) and vitamin E.
Camelina oil is used externally for skin, body, and hair care. Its consumption also helps fight free radicals, reduce inflammation, lower cholesterol levels, and improve diabetes.
Like agave or hemp, camelina is being studied as a potential biofuel. It could notably replace part of the kerosene used in aviation.
It has the advantage of being resistant and adaptable to all types of soil, even poor ones. Additionally, its cultivation cycle is very short (4 months), allowing for a quick harvest. It offers good yields: about 15 quintals/hectare.
It is also of interest in agriculture where it is cultivated as green manure to enrich the soil. Its flowers are also melliferous and attract many pollinators.
Nutritional Composition
- Amino acids
- Vitamins: pro-vitamin A, E
- Minerals and trace elements: potassium, calcium, iron, sodium
- Proteins
- Fibers
- Carbohydrates
- Fatty acids: omega-3-6-9
- Antioxidant agents: phytosterols, flavonoids, proanthocyanidins
The Benefits of Camelina
🍑 Improves Skin Beauty
Applied directly to the skin, camelina oil contributes to its beauty and health. It is particularly beneficial for sensitive and atopic skin, dry or mature skin. It helps to reduce facial redness, soothe skin inflammations, and relieve eczema and psoriasis.
Internally, its properties are equally beneficial for the skin. Camelina vegetable oil is very rich in vitamin E. Thanks to its antioxidant properties, it protects the skin from free radicals that accelerate skin aging. Vitamin E also has a reparative effect and helps maintain skin elasticity and plasticity.
Finally, the fatty acids in the oil nourish skin cells and strengthen the protective barrier. With about 40% of its composition, camelina oil is one of the richest vegetable oils in omega-3.
This review from North Carolina State University (USA) has examined plant oils, notably camelina oil, for skincare.
🥝 Antioxidant
The vitamin E in camelina effectively protects the body from free radicals and their damage. But its action is complemented by other antioxidant agents.
Camelina seeds contain phytosterols, flavonoids, and proanthocyanidins, also present in sorghum. These compounds prevent oxidation and reduce oxidative stress.
This study from Memorial University of Newfoundland (Canada), conducted directly in the laboratory, shows the antioxidant potential of camelina seeds.
🔥 Anti-inflammatory
Thanks to its richness in fatty acids, camelina has an anti-inflammatory effect. In addition to soothing skin inflammations, it can help relieve osteoarthritis, arthritis, and joint pain.
Camelina oil contains 2 types of omega-3: Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA). Once consumed, these are transformed into anti-inflammatory compounds (prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and eicosanoids).
Furthermore, camelina oil has a very good omega-3/omega-6 balance. However, an imbalance of these omegas can lead to an overproduction of pro-inflammatory substances.
This study from the University of Eastern Finland, conducted on humans, shows the anti-inflammatory action of camelina oil.
🍳 Reduces Cholesterol Levels
Regular consumption of camelina oil helps to reduce cholesterol levels. It notably lowers LDL-cholesterol (or “bad” cholesterol) which accumulates in the arteries. At the same time, camelina oil reduces blood triglyceride levels.
This action is due to its richness in omega-3 and polyphenols. These prevent cholesterol oxidation and its accumulation in the blood, leading to atherosclerosis.
This study from the University of Eastern Finland, conducted on humans, shows the cholesterol-lowering effect of camelina oil.
🍭 Improves Diabetes
Camelina is of great help in cases of diabetes mellitus and helps control blood sugar levels. On one hand, it lowers blood glucose levels. On the other, it improves insulin resistance and lipid metabolism.
This study from the Zaporozhye State Medical University (Ukraine), conducted on rats, shows the benefits of camelina in cases of diabetes.

How to consume camelina?
Camelina Oil
Camelina is most often offered in the form of vegetable oil, directly extracted from the plant’s seeds. We recommend choosing an oil from a first cold pressing which will be of better quality.
- In cooking, camelina oil is appreciated for its slight almond taste. It is used for seasoning vegetables and can also be added to smoothies and health drinks. However, it cannot be heated to preserve its active ingredients.
- In cosmetics, it is applied directly on the skin for body and face care or massages. Quickly absorbed, it leaves no greasy film. It is also a good hair oil that repairs damaged hair.
Camelina Seeds
Camelina seeds provide a good supply of fiber and vegetable proteins. They have a slight nutty, slightly grassy taste. They can be enjoyed as they are. You can sprinkle them on salads, add them to soups, yogurts, smoothies, and health drinks.

Camelina Flour
Camelina flour is obtained by grinding the press cakes, the residues from oil extraction. Reduced to powder, they provide a naturally gluten-free flour, rich in fiber and protein. This flour has a pleasant nutty taste and can be used for making bread, pasta, pizza doughs, etc. It is added at a rate of 5 to 30% of the preparation.
Consume sustainably: favor local, organic, and fair-trade camelina
✓ Camelina is grown in many regions of the world. It can be found in Europe (Germany, Italy, France…) as well as in Canada (Quebec). Although its cultivation became rare in the 20th century, it is experiencing a revival today. In France, camelina is mainly cultivated in the southeast, but also in the Occitanie region and the Massif Central like here, on the Velay plateau.
✓ Favor a French production from organic farming. Fair trade channels also support the work of producers.
Dosage
The recommended dosage is 1 tablespoon of camelina per day.
Contraindications and Side Effects
The consumption of camelina presents some contraindications:
- As a precautionary measure, it is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women and young children;
- Because it thins the blood, it is not recommended for those with hemophilia or those undergoing anticoagulant treatment.
The consumption of camelina has very few side effects. Only an allergic reaction may occur in case of sensitivity to plants of the Brassicaceae family.
If you experience any side effects, stop consuming it and consult a doctor.
Sources and scientific studies
Erin M. Moore, Charles Wagner, and Slavko Komarnytsky, 2020. The Enigma of Bioactivity and Toxicity of Botanical Oils for Skin Care.
Md Jiaur Rahman, Adriano Costa de Camargo, Fereidoon Shahidi, 2018. Phenolic profiles and antioxidant activity of defatted camelina and sophia seeds.
Vanessa D de Mello, Ingrid Dahlman, Maria Lankinen, Sudhir Kurl, Leena Pitkänen, David E Laaksonen, Ursula S Schwab, Arja T Erkkilä, 2019. The effect of different sources of fish and camelina sativa oil on immune cell and adipose tissue mRNA expression in subjects with abnormal fasting glucose metabolism: a randomized controlled trial.
Suvi Manninen, Maria Lankinen, Arja Erkkilä, Su Duy Nguyen, Maija Ruuth, Vanessa de Mello, Katariina Öörni, Ursula Schwab, 2018. The effect of intakes of fish and Camelina sativa oil on atherogenic and anti-atherogenic functions of LDL and HDL particles: A randomized controlled trial.



