What is it?
Folic acid, a vitamin belonging to the B group, is associated with various names. It is also called folates or vitamin B9. This element is present in large quantities in leafy vegetables, spinach, watercress, green beans, as indicated by its etymology.
Indeed, the terms folates and folic are derived from the Latin word folium, translated as ‘leaf’. Its intake is primarily ensured by diet.

Vitamin B9 is involved in cell renewal. Its effect on fetal development and its benefits during pregnancy are well recognized.
Specialists recommend that women of childbearing age and those wishing to have a child ensure a sufficient daily intake of folic acid.
Indeed, during the first trimester of pregnancy, folic acid contributes to the formation of the fetal nervous system and specifically ensures the closure of the neural tube. It also helps maintain overall health during childhood and adolescence.
The benefits of folic acid
Prescribed to women planning their pregnancy (starting two months before stopping contraceptives), folic acid performs several functions in the body:
- Involved in the process of amino acid renewal and DNA production.
- Contributes to the synthesis of cells that renew rapidly, such as skin cells, intestinal cells, white blood cells, or red blood cells.
- Stimulates growth during childhood and adolescence.
- Improves tissue healing.
- Strengthens the immune system.
- Plays a role in proper brain functioning, particularly in the nervous system, by synthesizing several neurotransmitters.
- During the first trimester of pregnancy, involved in the formation of the fetal nervous system, especially in the closure of the neural tube.
- During pregnancy, contributes to the growth of maternal tissues (blood flow, uterine enlargement).
- According to some studies, folic acid could help prevent certain cancers (breast, colon, stomach, pancreas, and lung cancer). This function remains to be proven.
Note: The intake of folic acid is recommended by specialists to avoid the occurrence of fetal malformations during pregnancy.
Symptoms of deficiency
Folic acid deficiencies can be due to a lack of dietary intake, malabsorption due to medication, or malabsorption (digestive disease).
Given its functions, folic acid deficiencies will cause typical symptoms, such as:
- Macrocytic anemia: red blood cells are too large
- Depressive disorders
- Cardiovascular disorders
- Increased blood pressure
- Arthritis
- Digestive disorders (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea)
- Neurological disorders, psychotic states
- In pregnant women, consequences of folic acid deficiencies can be serious: preterm delivery, delayed fetal growth, malformation of the fetal nervous system such as spina bifida (failure of closure of the posterior bony canal or spine) or anencephaly (failure of neural tube closure).
Recommended daily intake
The needs for folic acid are easily met by adopting a varied and balanced diet.
However, daily needs are greater for overweight individuals, children, and of course, pregnant women:
- Baby from 0 to 1 year old: 70 µg/day
- Child aged 1 to 3 years: 100 µg/day
- Child aged 4 to 6 years: 150 µg/day
- Child aged 7 to 12 years: 200 to 250 µg/day
- Child aged 13 to 15 years: 300 µg/day
- From 16 years old: 330 µg/day
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: 400 µg/day
Additional Information: Since the needs for vitamin B9 are much greater during pregnancy, specialists from the French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety (Anses) recommend supplementation in folic acid during pregnancy, at a level of 400 µg/day (starting two months before the start of pregnancy, until the end of the first month of pregnancy).
It is preferable to discuss with your primary care physician, your gynecologist, or your midwife before taking medication supplements.
Top 5 foods containing folic acid
A balanced diet (meats, fruits, and vegetables) ensures sufficient daily intake of folic acid. Here are five foods rich in vitamin B9.
1. Liver

Cod liver, veal liver, or lamb liver contains between 155 µg and 330 µg of folic acid per 100 g of meat. They are therefore nutritionally valuable.
Calf and lamb liver can be served well-done during the two main meals, accompanied by green vegetables and starchy foods, such as whole grains or potatoes. As a precaution, it is advised to avoid consuming them during pregnancy.
2. Green Vegetables

Green vegetables fit perfectly into everyday nutrition. Peas, green beans, salads (lamb’s lettuce, watercress), and spinach are rich in folic acid.
They are low in calories, so those with a big appetite can consume them in large quantities.
Cooked in water or steamed, they make excellent side dishes for meats and fish. They can also be eaten in salads, as a starter, or incorporated into main dishes (mixed salads).
Attention: folic acid is a water-soluble vitamin. It dissolves in cooking water. For better intake, prioritize steaming or favor foods that can be eaten raw.
3. Eggs

Eggs are a protein source. Athletes understand this well, consuming them regularly. Eggs also provide a significant source of folic acid.
A hard-boiled egg contains 106 µg of vitamin B9 per 100 g. Therefore, consuming one each morning ensures a regular intake of folic acid. Depending on preferences, eggs can be eaten cooked in a skillet, soft-boiled, or as an omelet.
Good to know: It is recommended not to consume more than five eggs per week. Egg yolk is indeed high in cholesterol.
4. Melon
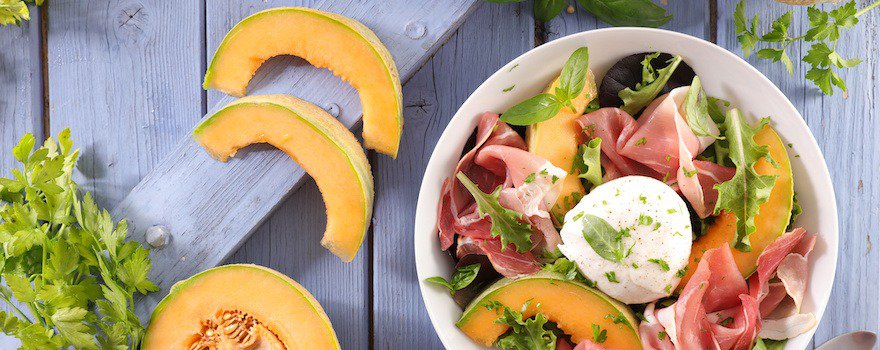
Melon is an ideal fruit during hot periods. Mainly composed of water, it is a refreshing food that enhances daily hydration.
Usually served as a starter, it can be eaten as is, cut into small pieces, with mozzarella or cured ham. It can also make an excellent fruit salad dessert or snack!
5. Chestnuts

Chestnuts are traditionally picked or gathered in the fall. Chestnuts contain 120 µg of folic acid per 100 g of food. They serve as a very nutritious snack.
Chestnuts can be cooked in water or roasted over a wood fire. For optimal vitamin B9 intake, prefer water cooking. They are also an interesting component for an original mash.
To accompany chestnut mash, opt for grilled red meat, game, or poultry (chicken, turkey). They also make a good stuffing for Christmas meats.
Note: Brewer’s yeast is the supplement with the highest folic acid content. With a concentration of 2,500 µg/100 g, it is a valuable nutrient for supplementing folic acid intake in cases of deficiency or malabsorption.
Regarding preservation, it’s useful to know that folic acid is sensitive to heat, light, and air. It’s advised to store folic acid-enriched foods away from light in a specially designated cupboard.
Dangers, adverse effects and folic acid overdose
According to experts, the recommended limit dose of folic acid is around 1 mg/day. Beyond this limit dose, the body experiences a folic acid overdose, which can lead to more or less pronounced neurological disorders.
It is therefore important that vitamin B9 supplementation is conducted under medical supervision to avoid the occurrence of undesirable effects.



